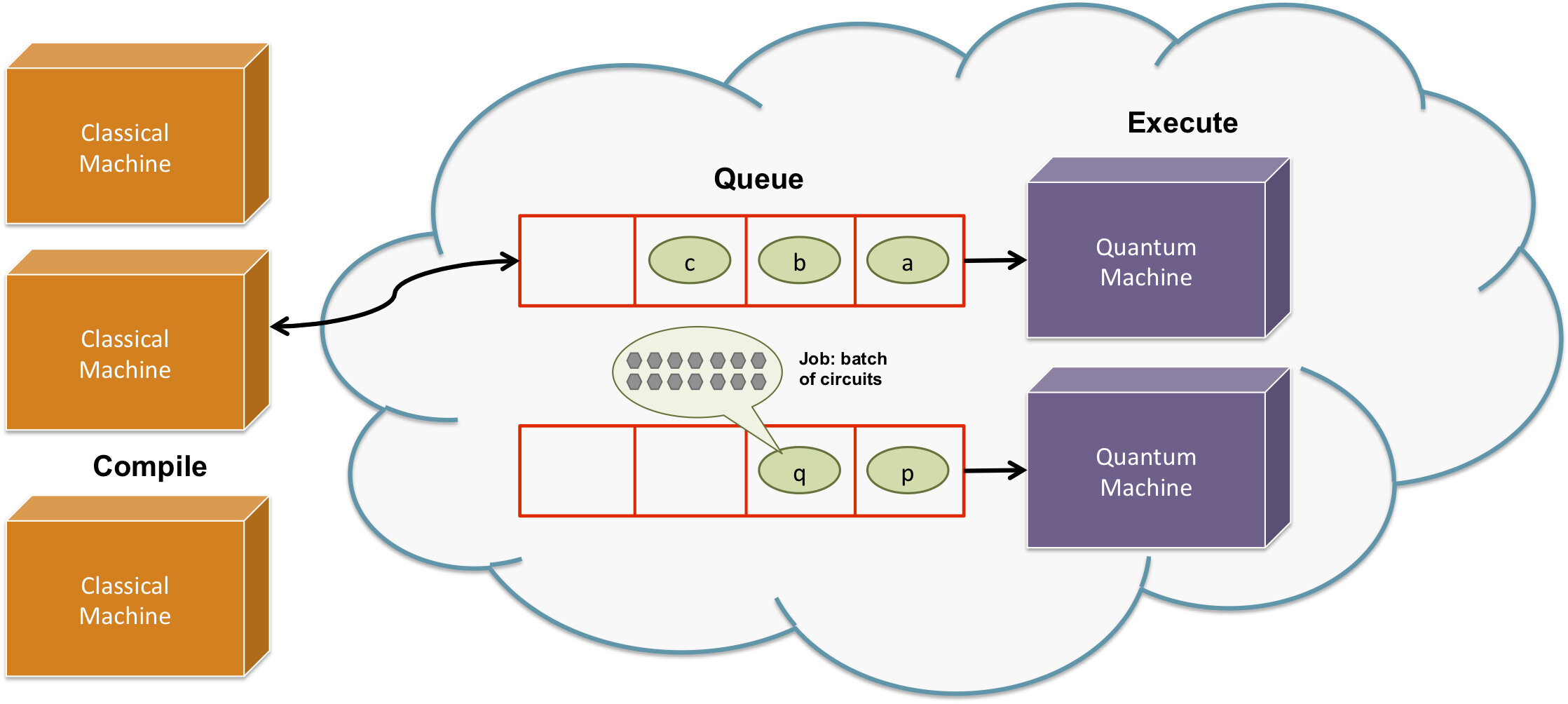
Clients launch quantum programs from their classical computers onto the vendor's quantum cloud wherein the jobs are queued until execution.
As the popularity of quantum computing continues to grow, quantum machine access over the cloud is critical to both academic and industry researchers across the globe. And as cloud quantum computing demands increase exponentially, the analysis of resource consumption and execution characteristics are key to efficient management of jobs and resources at both the vendor-end as well as the client-end. While the analysis of resource consumption and management are popular in the classical HPC domain, it is severely lacking for more nascent technology like quantum computing. This paper is a first-of-its-kind academic study, analyzing various trends in job execution and resources consumption / utilization on quantum cloud systems. We focus on IBM Quantum systems and analyze characteristics over a two year period, encompassing over 6000 jobs which contain over 600,000 quantum circuit executions and correspond to almost 10 billion "shots" or trials over 20+ quantum machines. Specifically, we analyze trends focused on, but not limited to, execution times on quantum machines, queuing/waiting times in the cloud, circuit compilation times, machine utilization, as well as the impact of job and machine characteristics on all of these trends. Our analysis identifies several similarities and differences with classical HPC cloud systems. Based on our insights, we make recommendations and contributions to improve the management of resources and jobs on future quantum cloud systems. DOI: 10.1109/IISWC53511.2021.00015
Gokul Subramanian Ravi, Kaitlin Smith, Pranav Gokhale and Frederic T. Chong